Brio™ Rechargeable IPG
| Brio™ Rechargeable IPG | |
|---|---|

|
|
| Category | Deep brain stimulation |
| Developer | St. Jude Medical, Inc. [1] |
| Announced | 2009 [1] |
| Released | Developers:
Consumers: 2009 [1] |
| Price | 19 150 USD [2] |
| Max output | 12.512.5 T 12.5 mA 0.0125 A mA[3] |
| Session duration | 0.050.05 s 8.333334e-4 minute s[3] |
| Scalp location | subthalamic nucleus, globus pallidus internus, ventral intermediate nucleus [4][5][6] |
| Weight | 29 g [1] |
| Controls |
Brio™ Patient Programmer, magnet [6] |
| Data available | |
| Risk factor | |
| Medical prescription | yes |
| https://www.sjmglobal.com/en-int/professionals/featured-products/neuromodulation/deep-brain-stimulation/implantable-pulse-generators/brio-ipg | |
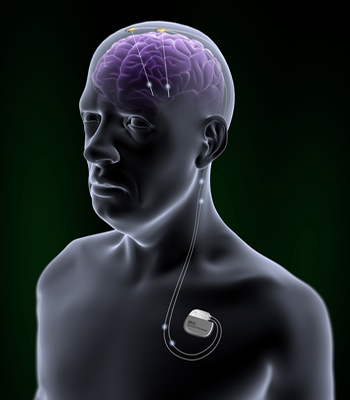
Brio™ Rechargeable IPG (Implantable Pulse Generator) provides deep brain stimulation therapy for patients suffering by Parkinson disease and essential tremor. It does not cure the diseases but it helps to reduce their symptoms. It is used primarily in the cases when the medication of the disease is not successful.[7]
The device was developed by St. Jude Medical, Inc. the company which focus on the medical devices and is settled in St. Paul, Minnesota.[8]
Contents
Main characteristics
Brio™ Rechargeable IPG was developed as a medical device which could provide treatment through deep brain stimulation. It is a standalone device and could be received only on prescription. It has to be implanted only on special clinics and the quality of surgery has a huge impact on the results of the treatment.[6] The device was approved by as a treatment of symptoms of Parkinson disease, essential tremor,[9] and Dystonia.[10]
The device consists of:
- Implantable pulse generator (IPG)
- Extensions
- Leads
- Patient programmer
- Patient magnet
- Charging system
The leads are implanted into the brain in accordance with the purposed treatment. The IPG is implanted on the upper part of the chest and could be controlled by patent programmer. Magnet could turn on or of the IPG.[6]
The IPG provides a long term brain stimulation. It contains a rechargeable battery. The device could be charged via antenna.[11] Brio™ Rechargeable IPG is a system which operate open-loop. It means that the IPG delivers continuous stimulation to patient's brain.[12] In addition, Brio™ Rechargeable IPG provides a constant-current stimulation, which means that the IPG deliver constant current to the brain. It is contrasted with voltage-controlled stimulation, in which the amount of affected tissue may vary.[5]
Purpose
The main purpose of the device is to treat the symptoms of certain incurable diseases and improve the patients' life in this way.
Company & People
The device was originally manufactured by St. Jude Medical, Inc, the company from St. Paul, Minnesota.[9] This company was however acquired by Abbott Laboratories in 2017.[13] Abbott Laboratories seats in Abbott Park, Illinois.[14]
- Miles D. White - Chairman and Chief Executive Officer of Abbott Laboratories
- Hubert L. Allen - Executive Vice President, General Counsel and Secretary of Abbott Laboratories[15]
- Michael T. Rousseau - President, Cardiovascular and Neuromodulation of Abbott Laboratories, former CEO of St. Jude Medical, Inc.[16]
Important Dates
- 1976 - the company St. Jude Medical, Inc. was founded.[17]
- 2009 - Brio™ Rechargeable IPG received CE (Conformité Européenne) mark of approval for treatment of Parkinson disease.[9]
- 2010 - Brio™ Rechargeable IPG was approved by the Australian Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA).[8]
- 2013 - Brio™ Rechargeable IPG received CE (Conformité Européenne) mark of approval for treatment of Dystonia symptoms.[10]
- 2015 - Brio™ Rechargeable IPG was approved by FDA.[7]
- 2017 - St. Jude Medical, Inc. was acquired by Abbott Laboratories.[13]
Enhancement/Therapy/Treatment
Parkinsons's disease
Essential Tremor
Dystonia
Ethical & Health Issues
http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/ner.12026/full
Public & Media Impact and Presentation
"There are no cures for Parkinson's disease or essential tremor, but finding better ways to manage symptoms is essential for patients," says Dr. William Maisel of the FDA. "This new device adds to the array of treatment options to help people living with Parkinson's and essential tremor enjoy better, more productive lives."[18]
Public Policy
Related Technologies, Projects or Scientific Research
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 St. Jude Medical. St. Jude Medical Receives CE Mark Approval for World’s Smallest, Longest-Lasting Rechargeable Deep Brain Stimulator for Parkinson’s Disease. Newswise, Inc [online]. 2009, Sep 9. Available online at: http://www.newswise.com/articles/st-jude-medical-receives-ce-mark-approval-for-world-s-smallest-longest-lasting-rechargeable-deep-brain-stimulator-for-parkinson-s-disease-first-patient-implanted-with-brio-neurostimulator-at-university-of-cologne-germany32 (Retrieved 6th April, 2017).
- ↑ Australian Government. Private Health Insurance (Prostheses) Rules 2015 (No. 1). Federal Register of Legislation [online]. Available online at: https://www.legislation.gov.au/Details/F2015C00649/Html/Volume_2 (Retrieved 6th April, 2017).
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Advanced Neuromodulation Systems, Inc. Brio™ Mozkový neurostimulátor: Manuál pro klinického lékaře. Cardion [online]. Available online at: http://www.cardion.cz/file/190/brio-klinicky-manual.pdf (Retrieved 6th April, 2017).
- ↑ OKUN, M. et al. Subthalamic deep brain stimulation with a constant-current device in Parkinson's disease: an open-label randomised controlled trial. The Lancet Neurology, 2012, 11(2), 140-149. Available online at: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1474442211703088 (Retrieved 6th April, 2017).
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 PREDA, F. et al. Switching from constant voltage to constant current in deep brain stimulation: a multicenter experience of mixed implants for movement disorders. European Journal of Neurology, 2016, 23(1), 190–195. Doi:10.1111/ene.12835 Available online at: http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/ene.12835/full (Retrieved 6th April, 2017).
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 St. Jude Medical. Brio™ Patient Programmer. U.S. Food and Drug Administration [online]. Available online at: www.accessdata.fda.gov/cdrh_docs/pdf14/P140009c.pdf (Retrieved 6th April, 2017).
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 U.S. Food and Drug Administration. FDA approves brain implant to help reduce Parkinson’s disease and essential tremor symptoms. U.S. Food and Drug Administration [online]. 2015, Jun 12. Available online at: https://www.fda.gov/NewsEvents/Newsroom/PressAnnouncements/ucm451152.htm (Retrieved 6th April, 2017).
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 St. Jude Medical. St. Jude Medical's Brio DBS system for treating Parkinson’s disease receives Australian TGA approval. News-Medical.Net [online]. 2010, Mar 23. Available online at: http://www.news-medical.net/news/20100323/St-Jude-Medicals-Brio-DBS-system-for-treating-Parkinsone28099s-disease-receives-Australian-TGA-approval.aspx (Retrieved 6th April, 2017).
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 BUSINESS WIRE. St. Jude Medical Receives CE Mark Approval for World’s Smallest, Longest-Lasting Rechargeable Deep Brain Stimulator for Parkinson’s Disease. BUSINESS WIRE [online]. 2009, Sep 9. Available online at: http://www.businesswire.com/news/home/20090909005095/en/St.-Jude-Medical-Receives-CE-Mark-Approval (Retrieved 6th April, 2017).
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 GUILLIOTTI, Kimberly. St Jude Medical’s Deep Brain Stimulation Trifecta: New Treatment Options for Dystonia in EU. MD Buyline [online]. 2013, Apr 23. Available online at: http://www.mdbuyline.com/st-jude-medicals-deep-brain-stimulation-trifecta-new-treatment-options-for-dystonia-in-eu/ (Retrieved 6th April, 2017).
- ↑ St. Jude Medical, Inc. Brio™ Rechargeable IPG: Avdanced Technology. St. Jude Medical, Inc. [online]. Available online at: https://www.sjmglobal.com/en-int/professionals/featured-products/neuromodulation/deep-brain-stimulation/implantable-pulse-generators/brio-ipg?halert=show&clset=92f57278-460e-4300-b7fe-89e52a04194f%3acadddb93-fcc4-47f2-8ceb-fd88f01ca17f (Retrieved 7th April, 2017).
- ↑ PICILLO, Marina, FASANO, Alfonso. Recent advances in Essential Tremor: Surgical treatment. Parkinsonism & Related Disorders, 2016, 22(1), S171–S175. DOI: 10.1016/j.parkreldis.2015.09.012 Available online at: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1353802015003879 (Retrieved 6th April, 2017).
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 St. Jude Medical, Inc. Abbott Acquisition of St. Jude Medical Set to Close on January 4, 2017. Jude Medical, Inc. [online]. 2016, Dec 30. Available online at: http://media.sjm.com/newsroom/news-releases/news-releases-details/2016/Abbott-Acquisition-of-St-Jude-Medical-Set-to-Close-on-January-4-2017/default.aspx (Retrieved 7th April, 2017).
- ↑ Abbott Laboratories. Contacts. Abbott Laboratories [online]. Available online at: http://www.abbott.com/contact.html (Retrieved 7th April, 2017).
- ↑ Abbott Laboratories. Executive Team. Abbott Laboratories [online]. Available online at: http://www.abbott.com/corpnewsroom/utilities/executive-team.html (Retrieved 7th April, 2017).
- ↑ Abbott Laboratories. Michael T. Rousseau. Abbott Laboratories [online]. Available online at: http://www.abbott.com/corpnewsroom/utilities/executive-team/michael-rousseau.html (Retrieved 7th April, 2017).
- ↑ St. Jude Medical, Inc. Our History: Investing in People and Ideas. St. Jude Medical, Inc. [online]. Available online at: https://www.sjmglobal.com/en-int/about/company-facts/history?clset=92f57278-460e-4300-b7fe-89e52a04194f%3acadddb93-fcc4-47f2-8ceb-fd88f01ca17f (Retrieved 6th April, 2017).
- ↑ MCINTOSH, James. Parkinson's brain implant approved by FDA. Medical News Today [online]. 2015, Jun 15. Available online at: http://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/295376.php?trendmd-shared=0 (Retrieved 7th April, 2017).