Difference between revisions of "Cyberdyne HAL"
(added links to research to save them for later use) |
(issues sections updated) |
||
| Line 48: | Line 48: | ||
== Enhancement/Therapy/Treatment == | == Enhancement/Therapy/Treatment == | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | Enhancement & Therapy - The exoskeleton can be used to restore the ability to walk in disabled patients and it can be also used to enhance the strength of a healthy human beyond their natural capabilities. | ||
== Ethical & Health Issues == | == Ethical & Health Issues == | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | We recorded no ethical or health issues connected to this particular device. | ||
| + | |||
| + | For more general issues connected with smartglasses, please see the [[Body-worn Wearables]] synopsis. | ||
== Public & Media Impact and Presentation == | == Public & Media Impact and Presentation == | ||
| Line 58: | Line 62: | ||
== Public Policy == | == Public Policy == | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | There is no policy regarding this particular device. However, policies relevant to [[Body-worn wearables]] may apply to this device too. | ||
== Related Technologies, Projects or Scientific Research == | == Related Technologies, Projects or Scientific Research == | ||
Revision as of 09:16, 16 May 2016
| Hybrid Assistive Limb | |
|---|---|
|
|
| Category | Limb-mounted |
| Developer | Cyberdyne [1] |
| Announced | 1997 (prototype)[2] |
| Released | Developers:
Consumers: (not released) |
| Price | 2000 USD (monthly)[3] |
| Operating system | (unknown) |
| Sensors |
bio-electric signals [4] |
| Weight | 12000 g (Lower-limb model, both legs)[4] |
| Controls |
user's brain signals [5] |
| Data available | Limited |
| Risk factor | Low |
| Standalone | |
| http://www.cyberdyne.jp/english/ | |
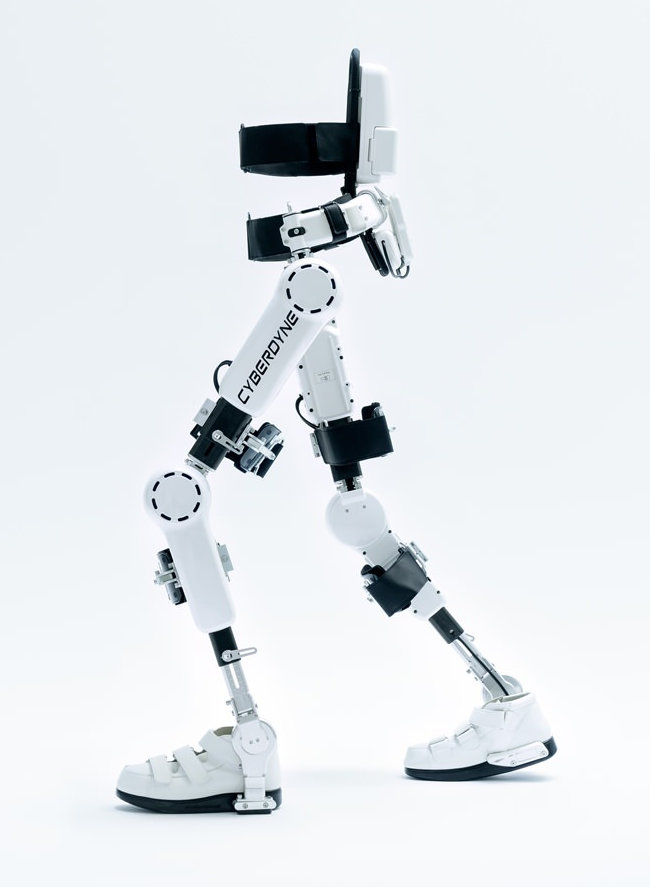
Cyberdyne Hybrid Assistive Limb, or HAL, is a powered, wearable exoskeleton designed to support and assist the muscles of the user. It is used to return the ability to move to persons who lost it due to spinal injury or a stroke. It can be used in mobility therapy and restoration, movement assistance for the elderly, and movement and strength enhancement for workers or incident response teams.
Contents
Main characteristics
Cyberdyne HAL is equipped with neurosignal sensors that pick up the neural signals from the user's spine and translate them into the movement of the motorized joints. The user is only required to think about moving their limbs. HAL is currently used in neuromuscular feedback therapy. There are also plans to develop a powered exoskeleton to enhance workers working with heavy weights,[6] or powered and protective exoskeleton for emergency and disaster responders.[7]
Purpose
Cyberdyne HAL is a powered exoskeleton used in mobility therapy and for movement and strength enhancement.
Company & People
The exoskeleton is developed by a Japanese company Cyberdyne Inc. The company was founded on 24 June 2004 and is headquartered in Tsukuba, Japan.[8]
- Professor Yoshiyuki Sankai - President and founder
- Fumiyuki Ichihashi, Shinji Uga, Hiroaki Kawamoto - Directors
Important Dates
Enhancement/Therapy/Treatment
Enhancement & Therapy - The exoskeleton can be used to restore the ability to walk in disabled patients and it can be also used to enhance the strength of a healthy human beyond their natural capabilities.
Ethical & Health Issues
We recorded no ethical or health issues connected to this particular device.
For more general issues connected with smartglasses, please see the Body-worn Wearables synopsis.
Public & Media Impact and Presentation
http://www.cyberdyne.jp/english/company/Media_list.html
Public Policy
There is no policy regarding this particular device. However, policies relevant to Body-worn wearables may apply to this device too.
Related Technologies, Projects or Scientific Research
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24704677
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpls/abs_all.jsp?arnumber=1545505
http://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.3109/17483107.2015.1129455
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpls/abs_all.jsp?arnumber=5953292&tag=1
http://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-642-34546-3_36#page-1
References
- ↑ http://cyberdyne.jp/english/company/Recruit.html
- ↑ http://web-japan.org/nipponia/nipponia38/en/feature/feature02.html
- ↑ http://www.theaustralian.com.au/news/world/robots-to-the-rescue-as-an-aging-japan-looks-for-help/story-e6frg6so-1226494698495
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 http://www.cyberdyne.jp/english/products/LowerLimb_nonmedical.html
- ↑ http://www.ccr-deutschland.de/en/healthcare/
- ↑ http://www.ccr-deutschland.de/en/2015/07/09/ondersteuning-van-de-arbeid/
- ↑ http://www.cyberdyne.jp/english/products/supporting.html
- ↑ http://www.cyberdyne.jp/english/company/index.html