Quell relief
| Quell relief | |
|---|---|

|
|
| Category | Limb-mounted |
| Developer | NeuroMetrix |
| Announced | Mar 2015 [1] |
| Released | Developers:
Consumers: May 2015 [2] |
| Price | 249 USD |
| Operating system | |
| Sensors |
N/A |
| Weight | 62 g |
| Controls |
smartphone |
| Data available | |
| Risk factor | |
| Standalone | |
| https://www.quellrelief.com/product | |
Quell is wearable device developed to provide palliative treatment for people suffering from chronic pain. Quell is commercially available; thus customers do not need a prescription from their doctor. At present, it is the only palliative wearable that is approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to be used during sleep. Quell wearable is presented with two technological improvements, which are OptiTherapy™ electrodes and transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS), a method that sends electrical pulses into afferent nerves through the skin. The technology of TENS is not new, but was developed on knowledge about possibility to heal with electricity, which was described previously in the 18th century.[3] The Quell device was constructed in the beginning of the 21st century basis on the knowledge of TENS[4] technology, marketing strategies, and usefulness for human enhancement and therapy.
Contents
Main Characteristics
The basic product a customer can buy, called the Quell Wearable Pain Relief - Starter Kit[5], includes a Quell device, adjustable sports band, charger cable, charger adapter, and two electrodes (the company claims this is a one-month supply). A manual is available to download in the Quell-user category, in both English and Spanis.
Users have to buy additional accessories like a travel bag, spare cables, charger adapter, and sports band.[6] Users have to also buy two electrodes regularly that are currently available in two kinds of packages: one package of two electrodes for 29.95 USD, or three packages of two electrodes for 89.85 USD[7].
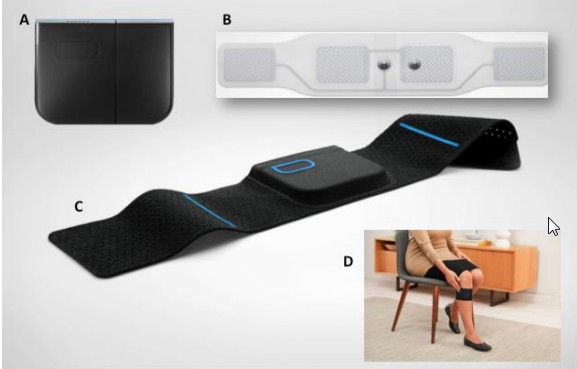
Regardless of which part of body is in pain, Quell is always placed on the upper calf (on either leg). There is better contact with nerves on this area of the body that send impulses to parts of the brainstem. After the device is fastened around the calf, users only need to press the button. The starter kit has a built-in accelerometer that allows calibration of electrical intensity according to the user's body; manual regulation is not needed.
For easier control, it is possible to download the Quell application for iOS[8] or Android[9]. The company also offers registration of individual user's devices; this will allow company to collect measured data about user and treatment process and create a database (this registration is optional).
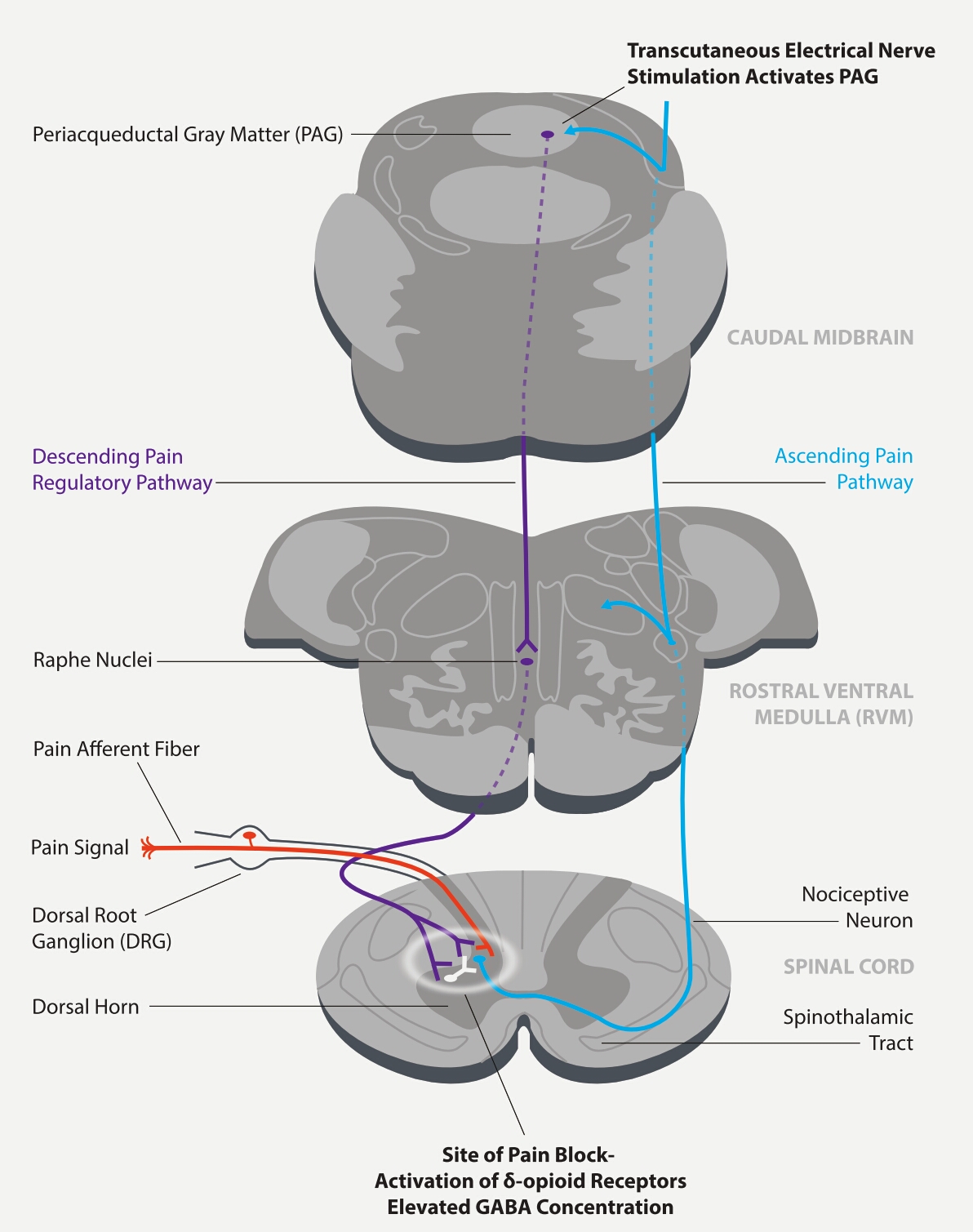
The mechanism of treatment lies in the following process: electrodes stimulate clusters of afferent sensory nerves, and this triggers the inhibition of pain in the brainstem. Inhibition comes up due to neurotransmitter release. This descending process starts in the periaqueductal grey matter, continuing to the medulla and then into the spinal cord (its dorsal horn).[10] Body-produced opioids- enkephalins-cause inhibition of pain signal transmission while activating δ-opioid receptors. The described process is the core of the reason why this treatment is cleared as 100% drug-free. A more detailed description regarding TENS technology (not Quell in particular) is available in Johnson's book Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation.[3]
The company also claims, that Quell is twice as strong as previous TENS pain relieving products; thus, it does not have to be used locally, but only on the upper calf.[11]
Purpose
Quell wearable is a device designated for the treatment of chronic pain, nerve disease and disrupted sleep.[13] It works on the principle of transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation that causes the release of endogenous opiates affecting pain relief.
Company & People
Neurometrix is a company directed at developing healthcare-wearable technology with a main focus on sleep disorders, chronic pain, and nerve diseases treatment. The company, located Waltham Massachusetts, was founded in 1996 as a spinoff of the Harvard-MIT partition of Health Sciences and Technology.[13][14]
Currently, Neurometrix offers four products in total:[13]
- Quell™: Wearable device for palliative purposes
- SENSUS®: Therapy device available by prescription. It is based on TENS technology for drug-free pain relief.
- DPNCheck®: Nerve conduction test for evaluating systemic neuropathies such as diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN), its detection, and monitoring.
- ADVANCE™ NCS System: Apparatus meant to assess neuropathy diagnosis.
Directors of Neurometrix include:[15]
- Shai N. Gozani, MD, PhD
- Allen Hinkle, MD
- David E. Goodman, MD
- Timothy R. Surgenor
- Nancy E. Katz
- David Van Avermaete
Important Dates
Important dates in the history of TENS include:
- 1759: John Wesley described medical usage of electricity for sciatica, headache, gout, and kidney stone treatment.[3]
- 1965: Melzack and Wall proposed the first conceptual model for mechanisms that could lead to pain relief. They rationalised that harmful signals may be inhibited by peripheral afferents of a large diameter.[3]
- 1970s: Development of TENS (Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation).[3]
- 2007: Johnson and Martinson-Largest meta-analysis of evidence claiming pain relief that was three times stronger pain than the placebo.[3]
Important dates of Quell device history include:
- 1996: Establishment of Neurometrix.[13]
- 2014: FDA gives a clearance to release Quell wearable device.[16]
Ethical Issues
At present, there are no ethical issues known. The purpose of a Quell device is to provide lenitive care (it is also cleared by the FDA). The device may help people from pain that has an unknown cause, and unknown ways of treatment. This can be considered a positive ethical value.
Also, no modification of the human body is involved except for the encephalins' stimulation: any long-term consequences for human organisms are not known.
Health Risks
The official statement from Neurometrix about side effects is that there are none. Usage is 100% drug-free, and was cleared in 2014 by the FDA.[16] No side effects are mentioned. There are some contraindications: patients with cardiac pacemakers or with implanted defibrillators should not use Quell, neither should people with implanted metallic or electronic devices.[17] Patients are supposed to consult with a doctor before using. Despite the mentioned contraindications, the Quell company says they have customers who have pacemakers and use the device successfully (see picture).
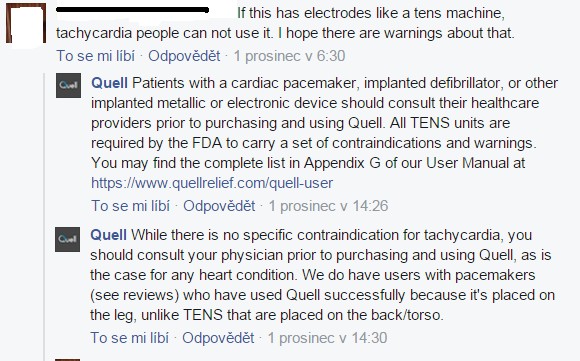
On the other hand, medication does not restrict Quell using.[18]
However, there are other information sources that discuss TENS technology. For example, they claim, that the TENS method is surely inexpensive and safe, but there are risks with using electrodes on damaged skin, or over a malignant area.[19] It could trigger a seizure in epileptic patient in cases where electrodes are put near a patient's head or neck.[20] Most of the patients may avoid these risks as Quell is used only on the upper calf. Nevertheless, we should wait for new quality scientific trials and to determine if the Quell device brings some currently unknown specific health risks.
Speculatively, it might happen that palliative treatment will only lead to pain elimination but not causation cure, which could cause grave injury. Let us consider, in a case of scoliosis, some physical workout could help to strengthen the back muscles and thus to stop back pain. Patients with any continuous body pain should take into consideration any ways to cure the cause of their pain first. This discussion is based on some videos and comments from people using Quell just for scoliosis.[21]
https://www.engadget.com/2017/07/10/opiate-addiction-quell-stimwave-triggr-health/
Enhancement/Therapy/Treatment
The Quell wearable device primarily has a therapeutic function. The company states it was developed for the purpose to palliate chronic pain that basically has origin in these four diseases:
However, diseases and illnesses are also identified treatable by TENS including: acute postoperative pain, primary dysmenorrhea, labour pain (which still remains controversial[22]), and post-stroke shoulder pain.
Although Quell was not created primarily to enhance cognitive or physical conditions in humans, it may have a secondary impact on physical and mental health (e.g., emotional stability, better memory) due to stress release, better sleep periods, and the ability to be more focussed once pain disappears. As a result, quality of life may be enhanced.
Public & Media Impact and Presentation
Regarding business interests in presenting this product to the public and considering the fact that the Internet is anonymous space where we have no clue who the author is of opinions or arguments, readers should consider that information may be false or a result of so-called trolling. This especially concerns possible health risks being hidden by promotion companies and institutions; furthermore, individual people could be receiving payment for competitive malignant, or otherwise praising a product untruthfully, or there may be people who just want to troll and thwart another project.
Company's Official Promotion
Products of Neurometrix are presented on official Neurometrix websites, and each of them also have their own webpage. It is questionable to what extent their websites can be trustworthy or customer-friendly due to the following reasons. It is non-transparency of information: It takes more time to find technical parameters or principles of mechanisms and useful information. The next reason is the absence of an ethical aspect in Quell devices. Customers will not see what the company thinks about such issues. The last reason is that the websites lack references to independent scientific studies that would critically evaluate the device's mechanism.
There is also an official launch video available on the Quell product website. In 2014, the official Quell Facebook page was launched, and it is still active. Also, its administrators show some effort in answering users' questions and to share new information with them. Quell also has its own YouTube channel; however, it contains only one video. Otherwise this channel seems to currently be inactive.
Other Mentions
There are some unofficial pages discussing Quell relief from the point of view of business, technology, and healthcare fields. In their articles, it seems these authors use promotional rhetoric, without mentioning any scientifically verified information. For example, read here in the article "Wearable of the Week: Quell Drug-Free Pain Relief Wearable" on Humavox).
Many advertising videos and testimonials are to be found on YouTube. Here are some examples:
The Internet medical journal MedGadget has released an independent review of Quell:
Likes:
- Utilizes scientifically-validated and medically-safe therapy for pain relief
- Aesthetically-pleasing and portable design
- Connects to an iPhone via Bluetooth to track sessions
Dislikes:
- Did not experience significant pain relief after two weeks of use
- Users with better success might have difficulty finding the optimal setting due to limited programming options on both the device and app
- You’ll need to spend $30 on extra electrode strips[25]
MedGadget's conclusion is that 'We unfortunately failed to find significant pain relief after using this $250 device for a few weeks, but much more testing is needed before we can come to a definite conclusion'.[25] However, MedGadget does not provide any specific data to support their claims about the disadvantages.
Besides other official presentations, many individual users share their experiences with the device on their blogs or Facebook posts, comments, ratings and so on. Blog contributors describe using Quell mostly as a positive experience. People are not satisfied with the fact that the insurance is not included, that there is hardly any available information, and that the expensive electrode needs to be changed more than it is officially stated, along with other inconsistencies. For example, a user claims '...the replacement electrodes cost $30 for 2 ($15 each) and each one is supposed to last 2 weeks, however, I used my first one for exactly 4 weeks before it stopped working as well'.[26]
Individual users' manual- or testimony-like videos can be found as well. here, the users claim no affiliation with the company: Quell Wearable Pain Relief For Sciatica Review And Walkthrough, 7. 7. 2015
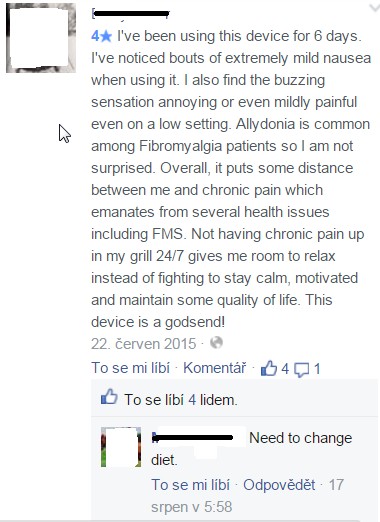
The only health issue found was nausea, although a patient claimed pain reduction (see picture below): this claim is actually the only one that neither the Quell site nor Dr. Shai Gozani has responded to. However, there is no evidence if this is really a side-effect of Quell usage.
People also comment intensity of pain reduction. Results may vary from experiencing a fully satisfying treatment, to partial improvement or no advances in pain relief at all (see pictures from the YouTube chat[27]).
Below are examples of various blogs with articles dealing with Quell:
Public Policy
Quell received clearance from the FDA, that is a federal agency that is part of the Department of Health and Human Services in the US. Quell is kept under regulation number 882.5890, and it is identified as 'a transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulator for pain relief [and] a device used to apply an electrical current to electrodes on a patient's skin to treat pain'.[28] Further, it is classified as a "Class II (performance standards)".[28] The latter category features most medical devices (FDA has stated 43%), including wheelchairs or pregnancy test kits, for example.[29]
Related Technologies, Projects, or Scientific Research
WINS Technology
Neurometrix says they use so called Wearable Intensive Nerve Stimulation (WINS);[30] however, no studies are provided to explain its mechanisms.
TENS Research
There is only one paper about Quell principles on the official Quell website,[4] but this does not contain the necessities of an independent scientific study. Although there are no other studies dealing with Quell products specifically, independent research about transcutaneous electric nervous stimulation (TENS) was conducted. This study appears to not be unambiguous regarding good efficacy of TENS in treatment. The following are a few works engaged in TENS technology and its influence on different diseases.
Sluka and Walsh[22] summarise existing research of TENS and shows a couple of results regarding scientific trials. They speak about equivocal effectiveness remaining low due to the number of randomised and controlled trials. Sluka and Walsh quote that different trials for one disease may have contrasting results, as in cases of treating labour pain.[22]
Mark I. Johnson is the author of a book supporting TENS technology.[3]
References
- ↑ NeuroMetrix Launches Indiegogo Campaign for Quell™ Wearable Pain Relief Technology: http://investor.neurometrix.com/releasedetail.cfm?ReleaseID=899167, December 15, 2015
- ↑ NeuroMetrix Announces First Shipments of Quell™ Wearable Pain Relief Device: http://investor.neurometrix.com/releasedetail.cfm?releaseid=912945, December 15, 2015
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 3.6 Johnson, Mark I., Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS): Research to support clinical practice, Oxford University Press, 2014
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Science Behind Quell™ Wearable Pain Relief Technology for Treatment of Chronic Pain: https://www.quellrelief.com/files/science-behind-quell.pdf, (Retrieved Dec 15, 2015)
- ↑ Quell wearable pain relief, starter kit, online shop webpage: https://store.quellrelief.com/products/quell-wearable-pain-relief
- ↑ Quell, Accessories, Online shop webpage: https://store.quellrelief.com/collections/accessories
- ↑ Quell, Electrodes, Online shop webpage: https://store.quellrelief.com/collections/electrodes
- ↑ Quell relief application available to download: https://itunes.apple.com/app/quell-relief/id972079954
- ↑ Quell relief application available to download on GooglePlay: https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.neurometrix.quell
- ↑ Introducing Quell™, a 100% drug free technology proven to fight pain: https://www.quellrelief.com/files/Quell%20HCP%201%20page%20(3).pdf
- ↑ NeuroMetrix Investor statement: http://investor.neurometrix.com/releasedetail.cfm?releaseid=923300, December 15, 2015
- ↑ Introducing Quell, a 100% drug free technology proven to fight pain: https://www.quellrelief.com/files/Quell%20HCP%201%20page%20(3).pdf
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 13.2 13.3 Neurometrix, Company overview: http://www.neurometrix.com/about-neurometrix/company-overview.html, (Retrieved Dec 15, 2015)
- ↑ NeuroMetrix Launches Quell™ Wearable Pain Relief Technology: http://www.businesswire.com/news/home/20150615005489/en/
- ↑ Neurometrix, Board of directors: http://www.neurometrix.com/about-neurometrix/board-of-directors.html
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 NeuroMetrix Begins Shipping Quell Device, June 1, 2015: http://www.fdanews.com/articles/171428 (Retrieved Dec 15, 2015)
- ↑ Frequently Asked Questions by Clinicians: https://www.quellrelief.com/clinicians, December 15, 2015
- ↑ Quell relief official website, Clinicians: https://www.quellrelief.com/clinicians
- ↑ Searle, R.D., Bennett M.I., Johnson M.I., Callin S., Radford H., Letter to editor: transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) for cancer bone pain. Palliat Med, 2008; 22 : 878 - 9
- ↑ Jones, Iain, Johnson Mark I., Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation, 2009
- ↑ Quell Wearable Pain Relief For Sciatica Review And Walkthrough, in: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BHI7PSxXbSw, (retrieved 12/8/2015)
- ↑ 22.0 22.1 22.2 Sluka KA, Walsh D., Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation: basic science mechanisms and clinical effectiveness, in: Journal of Pain, 2003, p. 109-121
- ↑ Quell Wearable Pain Relief For Sciatica Review And Walkthrough: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BHI7PSxXbSw, 7. 7. 2015
- ↑ Quell Wearable Pain Relief For Sciatica Review And Walkthrough: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BHI7PSxXbSw, 7. 7. 2015
- ↑ 25.0 25.1 Hands-on with Quell Wearable Pain Relief Device: http://www.medgadget.com/2015/08/hands-on-with-quell-wearable-pain-relief-device.html, (Retrieved Dec 15, 2015)
- ↑ Comment placed by Gina McNabb, in: http://www.painnewsnetwork.org/stories/2015/7/22/wear-tear-care-the-quell-pain-relief-device, 12/8/2015
- ↑ Quell Wearable Pain Relief For Sciatica Review And Walkthrough: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BHI7PSxXbSw, 7. 7. 2015
- ↑ 28.0 28.1 Code of Federal Regulations, Title 21, Volume 8, 21CFR882.5890 http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cdrh/cfdocs/cfCFR/CFRsearch.cfm?FR=882.5890
- ↑ Medical device classification list on: http://www.fda.gov/MedicalDevices/ResourcesforYou/Consumers/ucm142523.htm
- ↑ Main page of Quell relief: https://www.quellrelief.com/, (Retrieved Dec 15, 2015)