Difference between revisions of "Halo Sport"
(a correction) |
(Important Dates) |
||
| Line 60: | Line 60: | ||
== Important Dates == | == Important Dates == | ||
| + | |||
| + | * 2013 - Halo Neuroscience was created <ref> Infinite Power Solutions. Halo Neuroscience Review – Pulse Energy Headphones?. Infinite Power Solutions [online]. Available online at: http://www.infinitepowersolutions.com/halo-neuroscience/ (Retrieved 1st November, 2016).</ref> | ||
Revision as of 13:03, 1 November 2016
| Halo Sport | |
|---|---|

|
|
| Category | Transcranial direct-current stimulation |
| Developer | Halo Neuroscience |
| Announced | May 2014 [1] |
| Released | Developers: 2014 [2]
Consumers: October 2016 [3] |
| Price | 549 USD (Fall 2016)[4] |
| Max output | 2.0 mA2 T 0.002 A [4] |
| Session duration | 1800 s30 minute [5] |
| Scalp location | C3 and C4 or Cz [6] [7] |
| Weight | g |
| Controls | |
| Data available | Good |
| Risk factor | Low |
| Medical prescription | No |
| https://www.haloneuro.com | |
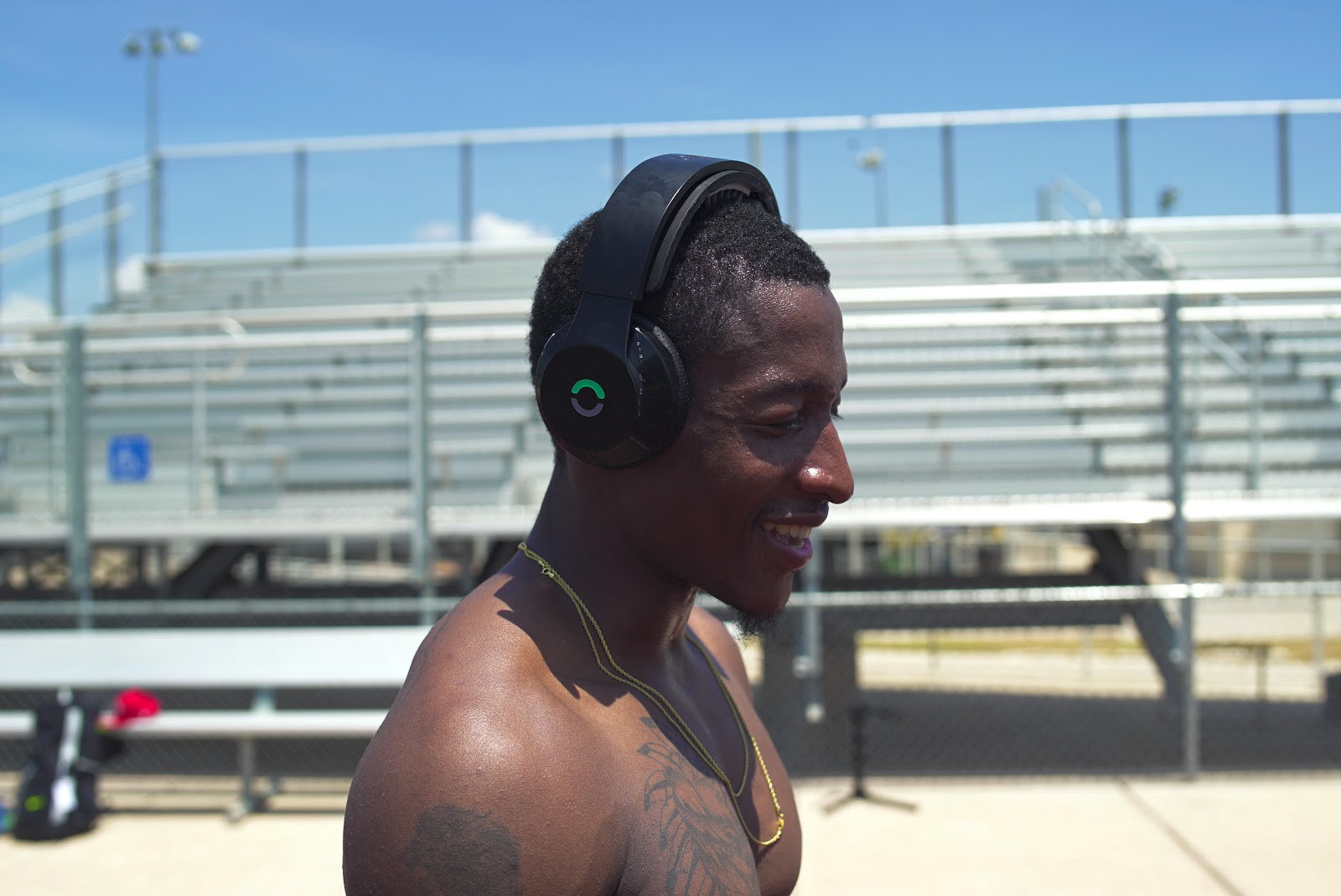
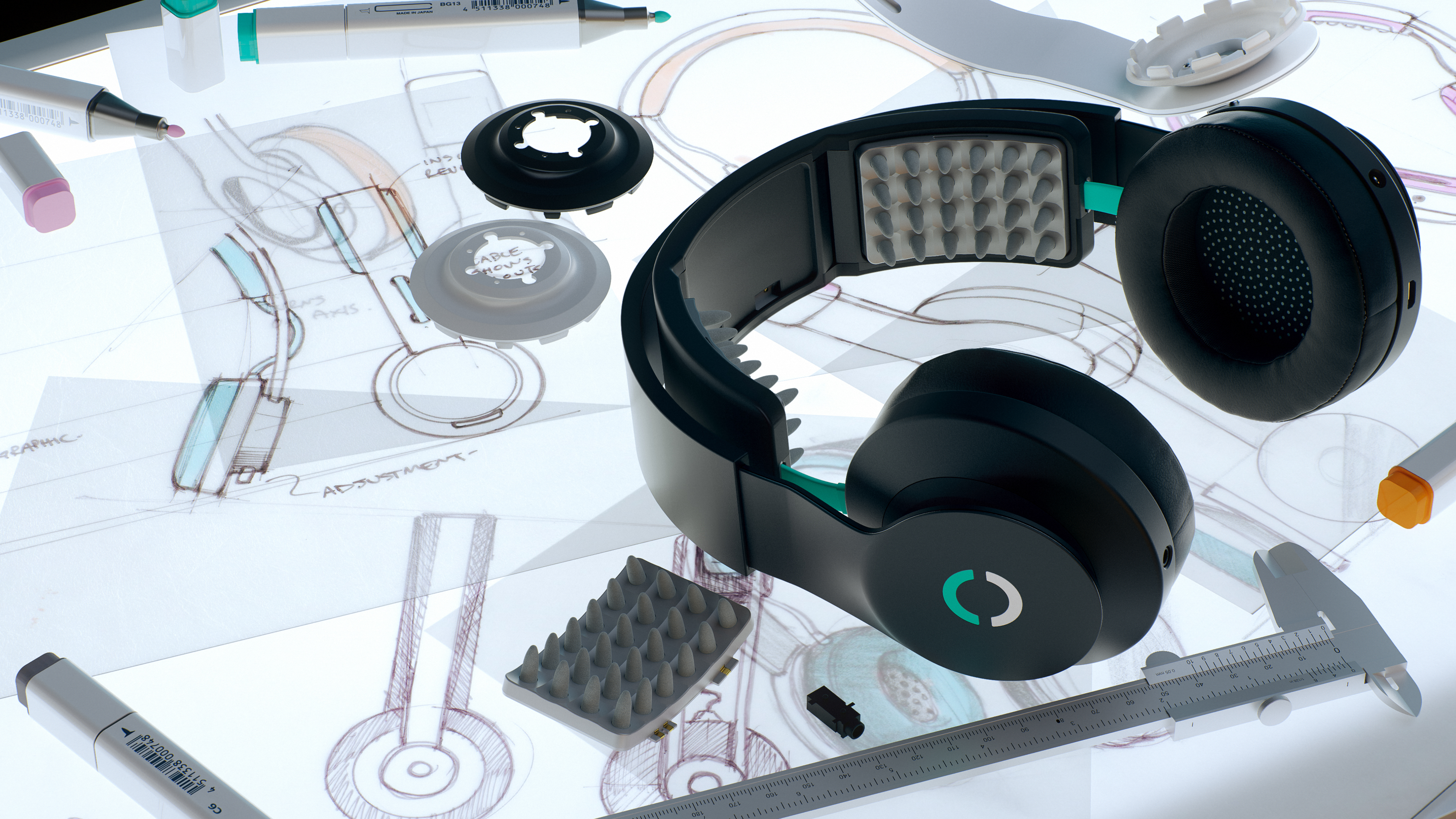
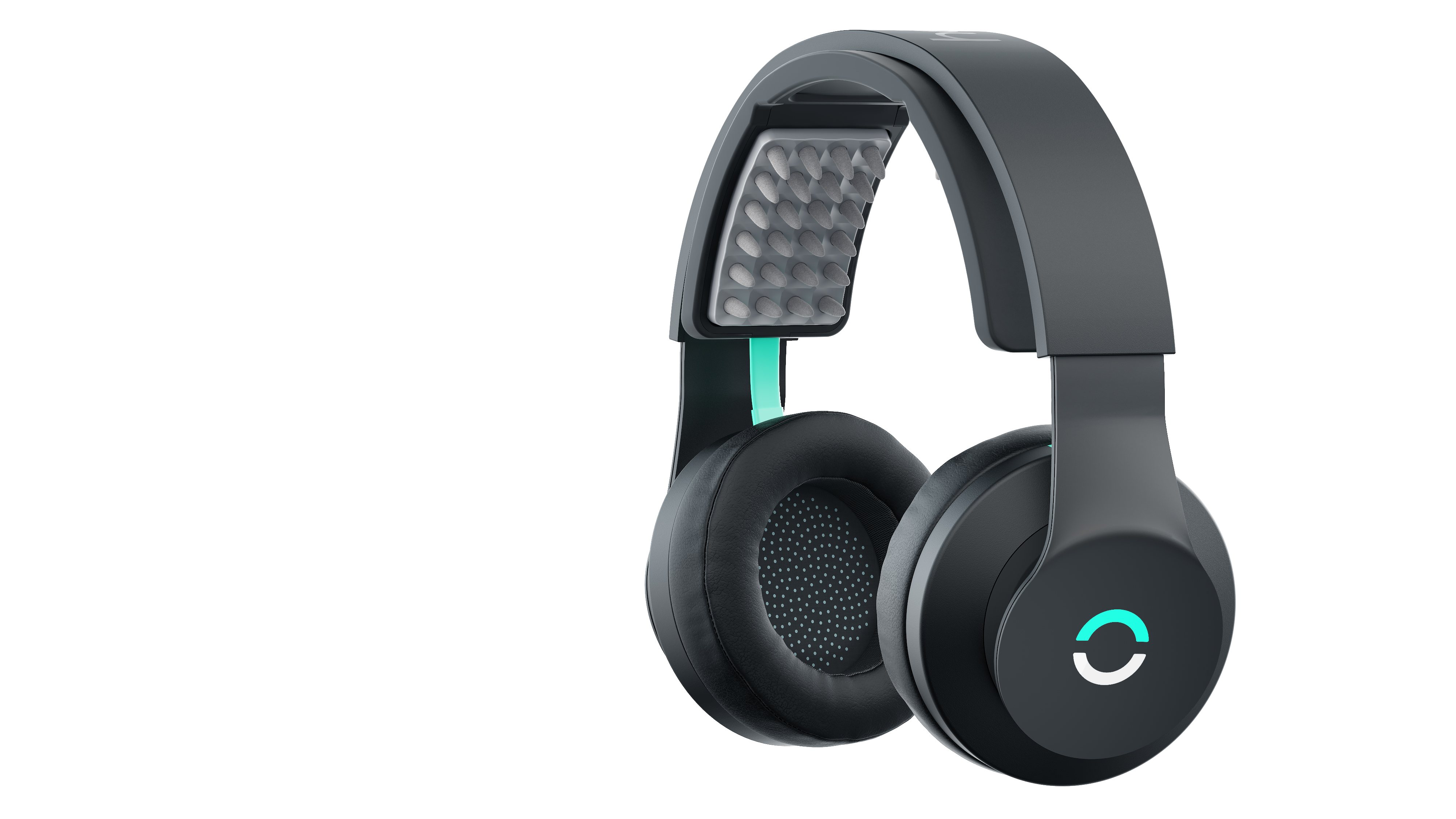
Halo Sport is head mounted device, which provides transcranial direct-current stimulation (tDCS). It was created by Halo Neuroscience as a tDCS device, which could be safely used outside laboratories. The device consists of a wearable headset on which are placed two electrodes and a neurostimulator, which is powered by battery.[9] The electrodes are entitled "primers" by Halo Neuroscience and tDCS is reffered as "neuropriming".[8]
The device stimulates motor cortex. If it is used during a training, it is supposed to enhance motoric abilities of its users,[10] which could make the training more effective. This feature was appraised by several sport organizations as US Ski and Snowboard Association, Michael Johnson Performance, or Invictus that take a part in Halo Sport's testing.[4] Halo Sport is also used by U.S. Department of Defense for improving skills of special operations forces.[11]
Contents
Main characteristics
Halo Sport is standalone fully enclosed device. It contains headset where are placed two or three electrodes. The electrodes are placed at C3, C4[6] resp. Cz[7]. In contrast to other transcranial direct-current stimulation's devices the position of electrodes is settled. Electrodes can be removed, but not placed to any other location on scalp.
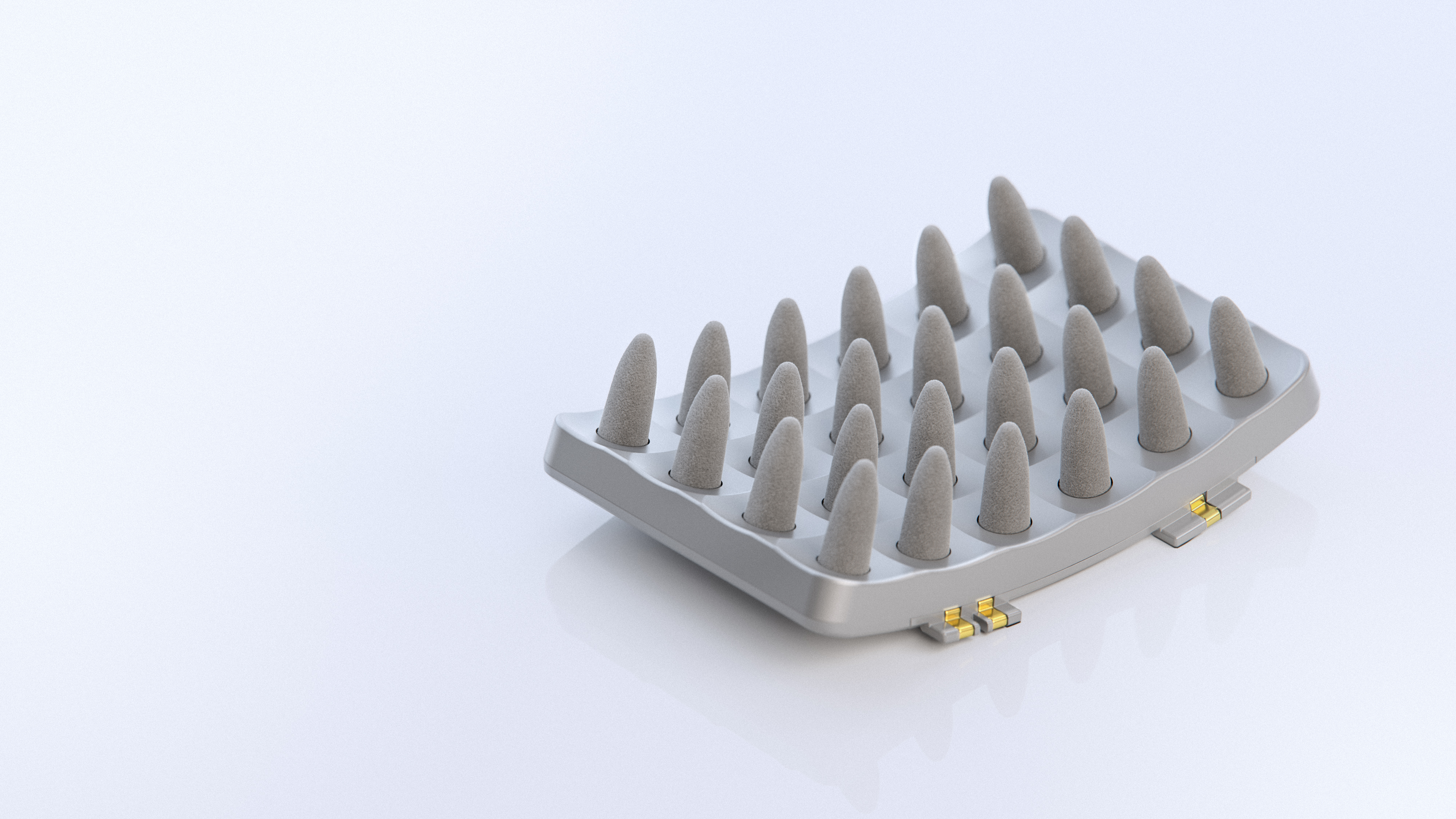
Electrodes must be changed after three month's use.[12] They consist of foam spikes.[5]
Purpose
The main purpose of the device is to enhance physical abilities of its user through tDCS.
Company & People
- Daniel Chao - co-founder and CEO of Halo Neuroscience
- Brett Wingeier - CTO of Halo Neuroscience
- Amol Sarva - co-founder and Board Member of Halo Neuroscience
- Reed Hundt - adviser
- Susan Paley - adviser
- Gary Abrams - adviser
- Nick Drake - adviser
- Mark George - adviser
- Andy Walsh - adviser
- Mario Schlosser - adviser[13]
Important Dates
- 2013 - Halo Neuroscience was created [14]
Enhancement/Therapy/Treatment
Halo Sport was approved by FDA as the device which can help patients to recover physically after stroke.[5]
Ethical & Health Issues
Besides a great amount of studies, tDCS technology on which is based Halo Sport it is not certain that tDCS is not harmful.[5] Sarkar, Dowker and Kadosh's experiments suggest that tDCS could have a negative impact on human cognitive abilities. Namely, they claim that the individuals in experiments show decrease in executive control in a flanker task.They argue:
Another important finding is that tDCS effects may be associated with cognitive costs in other domains. Poorer executive control in a non-mathematical, nonanxiety-inducing task after real compared with sham stimulation suggests that tDCS, while advantageous in certain contexts, may impair processes dependent on the stimulated region.[15]
The similar results were also published by Teresa Iuculano and Roi Cohen Kadosh, who point out that enhancement of certain congnitive ability could impaired other cognitive abilities.[16]
Amol Sarva reports that a wrong placement of electrodes could be harmful as he found during the initial tests of their new device:
"I turned it on and there was this bright flash and then I was basically blind," he told me. The test had sent a direct blast into his optic nerve. "Luckily it cleared up after a few minutes," says Sarva. "We're much better informed now about which parts of the brain we need to stimulate."[17]
Nonetheless, the position of electrodes is settled in the device they shipped.
Public & Media Impact and Presentation
Daniel Chao and Brett Wingeier worked together in NeuroPace on the RNS® System device. However, Chao claims that they wanted to develop a device which could affected more people and which installation would not be so invasive. “Our NeuroPace device was an elegant way to manipulate neurons, but barbaric to install,” he says. “Brett and I thought we could do better.”[5] Therefore, they founded with Amol Sarva Halo Neuroscience and after reaching FDA approval they introduced Halo Sport.
Funding.
There are still doubts whether tDCS is really effective.[3] Regarding Halo Sport, the user gi67 at Reddit points out that Olympians who declared that they had used Halo Sport during their training, did not significantly succeed in Olympics games: "Did tDCS enhance training? Maybe, maybe not. But no outstanding performance could be attributable to tDCS."[18] However, the user ohsnapitsnathan claims: "I think it's quite possible that tDCS use is actually much more widespread than this group and many athletes are just quiet about it because of the stigma of using "performance enhancing" technology."[19]
Other issue is the possibility that tDCS stimulation of motor cortex could be considered as a doping. However, no public policy against tDCS devices has been stated yet. WADA (the World Anti-Doping Agency) and the International Olympic Committee are still considering whether these kind of devices should be prohibited and collect information about them.[20]
Public Policy
A medical use of the device was approved by FDA.[5] WADA or the International Olympic Committee have not provided any conclusive claim about tDCS devices yet.[20]
Related Technologies, Projects or Scientific Research
References
- ↑ WEXLER, Anna. A pragmatic analysis of the regulation of consumer transcranial direct current stimulation (TDCS) devices in the United States. Journal of Law and the Biosciences [online]. 2015, Oct 12. Available online at: http://jlb.oxfordjournals.org/content/2/3/669.full.pdf+html (Retrieved 1st November, 2016).
- ↑ BROWN, Ayliffe. Neurotechnology To Unlock Human Potential: Interview with Halo Neuroscience CEO, Dr. Daniel Chao. Wearable Technologies [online]. 2016, June 28. Available online at: https://www.wearable-technologies.com/2016/06/neurotechnology-to-unlock-human-potential-interview-with-halo-neuroscience-ceo-dr-daniel-chao/ (Retrieved 31st August, 2016).
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 STICKLAND, Eliza. Olympic Athletes Are Electrifying Their Brains, and You Can Too. IEEE Spectrum [online]. 2016, Aug 23. Available online at: http://spectrum.ieee.org/biomedical/bionics/olympic-athletes-are-electrifying-their-brains-and-you-can-too (Retrieved 12th September, 2016).
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 BARNWELL, Aliya. This crazy new wearable uses 'neurostimulation' to prime your brain and body for exercise. Digital Trends [online]. 2016, Mar 11. Available online at: http://www.digitaltrends.com/wearables/neurostimulation-headphones-boost-workout-effectiveness/ (Retrieved 1st September, 2016).
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 5.5 MANEY, Kevin. Halo claims to make you jump higher, think faster, remember longer. Newsweek [online]. 2016, Feb 10. Available online at: http://europe.newsweek.com/halo-neuroscience-brain-stimulation-424829?rm=eu (Retrieved 1st November, 2016).
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 Halo Neuroscience. Bihemispheric Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation with Halo Neurostimulation System over Primary Motor Cortex Enhances Rate of Force Development in an Isometric Lateral Pinch Force Task. Halo Sport [online]. 2016, Feb 10. Available online at: https://halo-website-static-assets.s3.amazonaws.com/whitepapers/mvc.pdf (Retrieved 2nd September, 2016).
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Halo Neuroscience. A Real World Investigation into the Benefits of Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation to the Primary Motor Cortex on Muscular Performance in Elite Athletes. Halo Sport [online]. 2016, Feb 10. Available online at: https://halo-website-static-assets.s3.amazonaws.com/whitepapers/mjp.pdf (Retrieved 2nd September, 2016).
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Halo Neuroscience. Halo Sport Set Up. Halo Sport [online]. Available online at: https://www.haloneuro.com/set-up (Retrieved 2nd September, 2016).
- ↑ Halo Neuroscience. Bihemispheric Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation with Halo Neurostimulation System over Primary Motor Cortex Enhances Fine Motor Skills Learning in a Complex Hand Configuration Task. Halo Sport [online]. 2016, Feb 10. Available online at: https://halo-website-static-assets.s3.amazonaws.com/whitepapers/cct.pdf (Retrieved 2nd September, 2016).
- ↑ Halo Neuroscience. Media & Press. Halo Sport [online]. Available online at: https://www.haloneuro.com/press (Retrieved 2nd September, 2016).
- ↑ Halo Neuroscience. Department of Defense Selects Halo Sport to Train Special Ops Forces. Halo Neuroscience Company News [online]. 2016, Aug 4. Available online at: https://medium.com/halo-neuroscience-company-news/department-of-defense-selects-halo-sport-to-train-special-ops-forces-e0fd3b8d8c6a#.no7clt9vr (Retrieved 2nd September, 2016).
- ↑ SAWH, Michael. Halo Sport headphones will zap an athlete's brain to train harder: Brain detecting wearable will prepare you for your next big session. Wareable [online]. 2016, May 10. Available online at: https://www.wareable.com/sport/halo-sport-headphones-zap-an-athletes-brain-to-train-harder-2691 (Retrieved 31st October, 2016).
- ↑ Halo Neuroscience. Company. Halo Neuroscience [online]. Available online at: <https://www.haloneuro.com/company> (Retrieved 12th September, 2016).
- ↑ Infinite Power Solutions. Halo Neuroscience Review – Pulse Energy Headphones?. Infinite Power Solutions [online]. Available online at: http://www.infinitepowersolutions.com/halo-neuroscience/ (Retrieved 1st November, 2016).
- ↑ SAKAR, Amar; DOWKER, Ann; COHEN KADOSH Roi. Cognitive Enhancement or Cognitive Cost: Trait-Specific Outcomes of Brain Stimulation in the Case of Mathematics Anxiety. J. NEUROSCI 34 [online]. 2014, Dec 10. Available online at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4261089/ (Retrieved 1st November, 2016).
- ↑ IUCULANO, Theresa; COHEN KADOSH, Roi. The Mental Cost of Cognitive Enhancement. J Neurosci 10 [online]. 2013, Mar 6. Available online at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3672974/ (Retrieved 1 st November, 2016).
- ↑ POPPER, Ben. The Halo headband wants to make you smarter by shocking your brain. The Verge [online]. 2014, Apr 30. Available online at: http://www.theverge.com/2014/4/30/5668086/halo-neuroscience-brain-stimulation-funding-andreessen (Retrieved 1st November, 2016).
- ↑ gi67. Halo and the Olympics. Reddit [online]. 2016, Aug 25. Available online at: https://www.reddit.com/r/tDCS/comments/4zi5f2/halo_and_the_olympics/ (Retrieved 12th September, 2016).
- ↑ ohsnapitsnathan. Halo and the Olympics. Reddit [online]. 2016, Aug 25. Available online at: https://www.reddit.com/r/tDCS/comments/4zi5f2/halo_and_the_olympics/ (Retrieved 12th September, 2016).
- ↑ 20.0 20.1 BENNETTS, Julian. I got an electrical charge put straight into my brain to explore the bizarre new frontier of doping in sport. The Telegraph [online]. 2016, Aug 19. Available online at: http://www.telegraph.co.uk/olympics/2016/08/19/i-got-an-electrical-charge-put-straight-into-my-brain-to-explore/ (Retrieved 12th September, 2016).